CAUSES/RISK FACTORS leading to the development of varicose veins include:
 Intrinsic:
Intrinsic:
- Heredity weakness of the valves, at critical points like SFJ, SPJ – develops in adult like
- Congenital: in Syndromic conditions with Venous Malformations – develops in childhood.
- Extrinsic/Environmental
- Prolonged standing
- Pregnancy
- Increasing age
- Mechanical obstruction to venous outflow
Risk Factors:
- Heavy lifting
- Prior superficial or deep vein clots
- Female gender
- Multiple pregnancies.
- Strong Family history of Varicose Veins
Venous Disease is usually quiet for many years before becoming a cause of problems. The nature of the symptoms depend on the size of the vein where pooling of blood occurs.
 GENERAL SYMPTOMS include:
GENERAL SYMPTOMS include:
- Swelling
- Pain OR Ache
- Exercise Intolerance
- Itching
- Burning Sensation/Paresthesias
- Night Cramps
- Skin Colour Changes AND
- ONLY Cosmetic Problems
Not all symptomatic patients are aware of their symptoms because the onset may be extremely gradual. After treatment, patients are often surprised to realize how much chronic discomfort they had accepted as normal.
Pain caused by venous insufficiency is often improved by walking or by elevating the legs in contrast to the pain of arterial insufficiency, which is worse with ambulation and elevation.
TYPES: Specific Problems depend on the size of the vessels that have the weakness
1. Trunk Veins – As name indicates it appears on main Trunks of great and small saphenous vein of legs, which are Thick, Bulging, and close to skin surface and appear unpleasant.


2. Reticular Veins – These vein are connecting branch veins and represent a network of red coloured veins.

3. Telangectasia/Thread Veins/Spider Veins – These are dilated venules and about 0.1 to 1 mm in diameter. Usually do not harm but treated for cosmetic purpose.
COMPLICATIONS:
 Dermatitis/Eczema: overlying skin becomes dark and scales are seen
Dermatitis/Eczema: overlying skin becomes dark and scales are seen- Phlebitis:
- Blood within the varicose veins clots causing blockage and pain
- Can be felt as a painful nodule
- Bleeding
- Distended vein caused stretching of the vein wall and overlying skin
Damaged skin breaks with minimal injury leads to bleeding.
 Venous Ulcer
Venous Ulcer
- Severe skin damage leads to a spontaneous wound
- Seen most commonly above the ankle, where the venous pressure is maximum

5. Lipodermoslcerosis
- Seen as a wood like hard leg (involved area)
- Occurs due to severe damage to skin and the underlying soft tissue
- Usually multiple episodes of ulceration and healing have occurred by this time
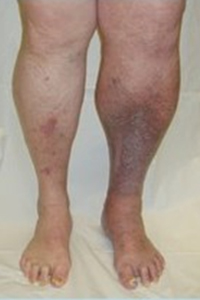
6. DVT & Post-Phlebitic Limb
- Involves clot formation in deep veins
- Leads to swelling of the foot
- Slippage of the clot to the chest can lead to serious breathing problems leading to an emergency.
- Permanent damage to valves in deep veins leads to post-phlebitic leg as seen in image to the Right

